Home / Abdominal pain / Digestive difficulties: symptoms, causes and remedies
Digestive difficulties: symptoms, causes and remedies
Difficulty with digestion, more correctly called ‘dyspepsia’, is often described simply as stomach ache, or indigestion.
It is a functional disorder, i.e. a medical condition that cannot be explained by an organic cause, a detectable anatomical impairment, but by alterations in the functioning of the body’s systems. Functional disorders are common but complex phenomena. Our organs, in fact, are interconnected, and these disorders can affect precisely the interactions between different organs, apparatuses and tissues, resulting in multiple and variable symptoms.
Even from this initial information, we can see that what we believe to be simply ‘’poor digestion‘’ is actually a less trivial complaint than we think.
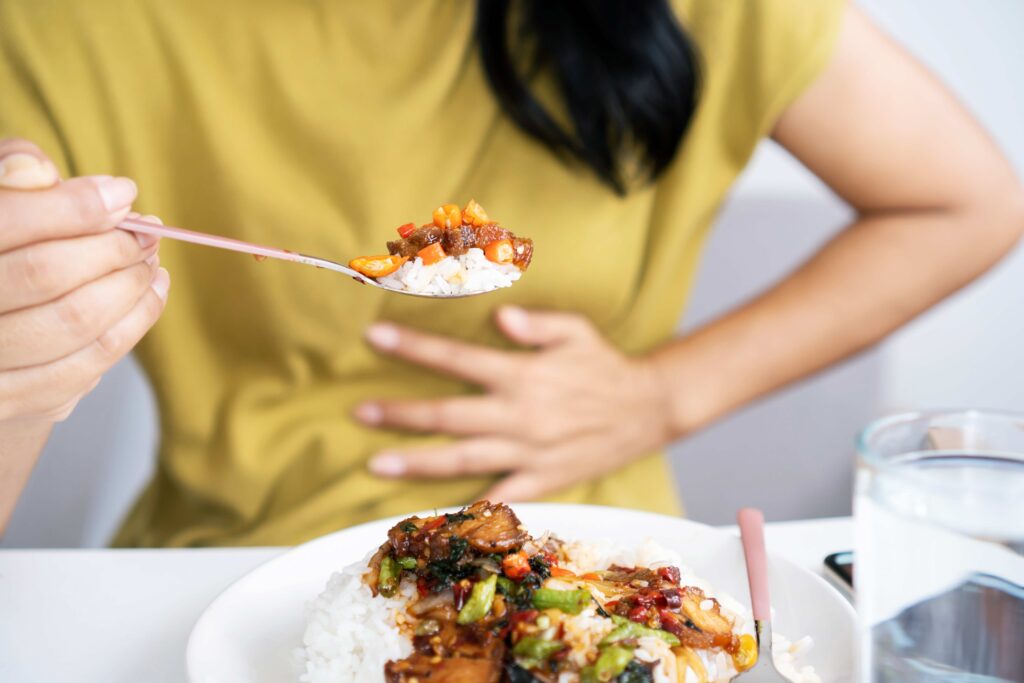
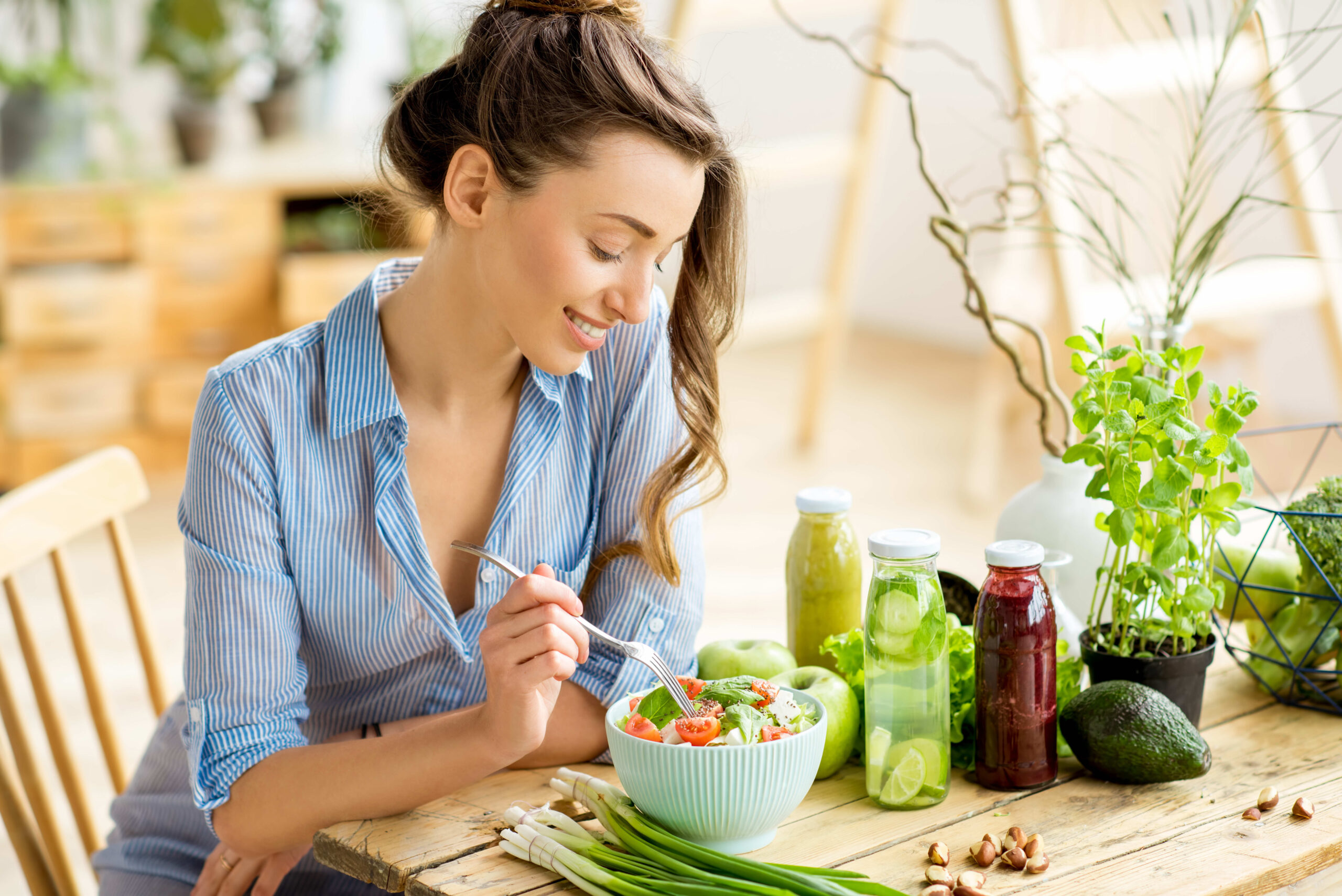


Poor digestion: what are the symptoms of dyspepsia?
Symptoms may occur occasionally (when eating more than usual, or at that particularly stressful business lunch) or be a constant in our lives. Regardless of the frequency with which they occur, the symptoms differ depending on the type of dyspepsia we suffer from. We often hear of nervous dyspepsia, or other types, but in reality, there are two clinically recognised types of dyspepsia:
- EPS (Epigastric Pain Syndrome). It is characterised by epigastric pain and/or burning in the ‘pit of the stomach’ and behind the sternum (heartburn), which can occur both on an empty stomach and after a meal.
- PDS (Postprandial Distress Syndrome). Symptoms are a feeling of fullness, heaviness, premature satiety, as if the food stays in the stomach for a particularly long time. It may also manifest with serious abdominal bloating, nausea or belching.
These symptoms may affect our day: we will tend to eat little and only certain foods, refuse invitations to lunches and dinners, we will not feel free to eat what we want, the feeling of bloating and heaviness may make us uncomfortable, and good days may end with a ‘bitter taste in the mouth’.
Causes of dyspepsia
But why do we struggle to digest? What causes dyspepsia? There can be many causes, including:
- Genetic and psychological factors
- Slowed gastrointestinal motility
- Visceral hypersensitivity
- Inflammation of the stomach mucosa
- Excess weight and obesity
- Pregnancy
- Inappropriate lifestyle and habits: stress, sedentary lifestyle, eating too fast, eating too much, poor nutrition.
In this regard, there are foods that can aggravate the situation, and those suffering from dyspepsia should avoid them:
- Coffee
- Carbonated drinks
- High-fat and fried foods
- Refined flours.
It is also worth keeping in mind, however, that the reaction to food in cases of dyspepsia is very subjective, so each person, with experience, will understand which foods to pay more attention to.


Remedies for dyspepsia
The prevention and treatment of dyspepsia can start at the table with eating habits.
It is advisable to:
- lose weight if you are overweight or obese
- eat slowly
- eat small, frequent meals
- steam, grill or bake
- eat more easy-to-digest foods such as: fish, fresh cheese and wholegrain cereals.
While these recommendations are important, they may not be enough in certain situations. It may be useful to treat dyspepsia with products appropriate to the problem. In any case, if the disorder recurs frequently, we recommend that you consult a health professional to understand which approach may be the most appropriate for the condition.




 it
it es
es en
en fr
fr be
be de
de pl
pl pt
pt ro
ro bg
bg be-nl
be-nl el
el he
he tr
tr